NEW QUESTION 26
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context dev
Context:
A CIS Benchmark tool was run against the kubeadm created cluster and found multiple issues that must be addressed.
Task:
Fix all issues via configuration and restart the affected components to ensure the new settings take effect.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the API server:
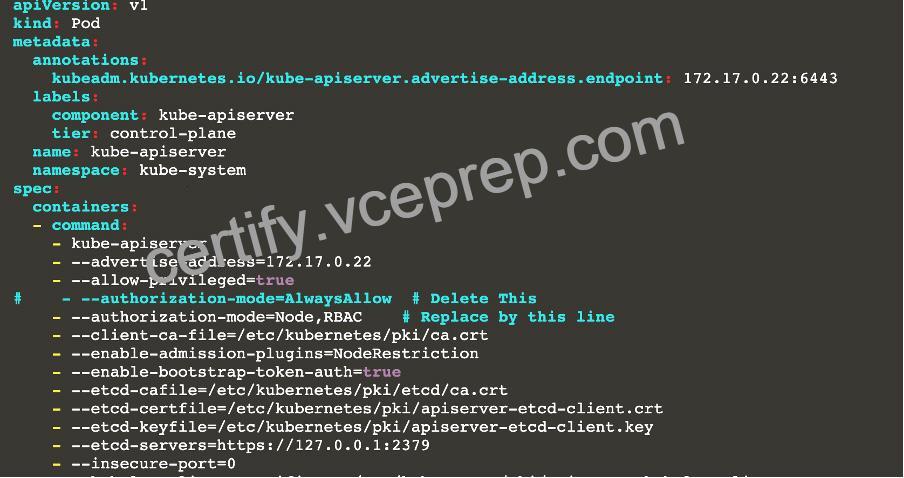
1.2.7 authorization-mode argument is not set to AlwaysAllow FAIL
1.2.8 authorization-mode argument includes Node FAIL
1.2.7 authorization-mode argument includes RBAC FAIL
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the Kubelet:
4.2.1 Ensure that the anonymous-auth argument is set to false FAIL
4.2.2 authorization-mode argument is not set to AlwaysAllow FAIL (Use Webhook autumn/authz where possible) Fix all of the following violations that were found against etcd:
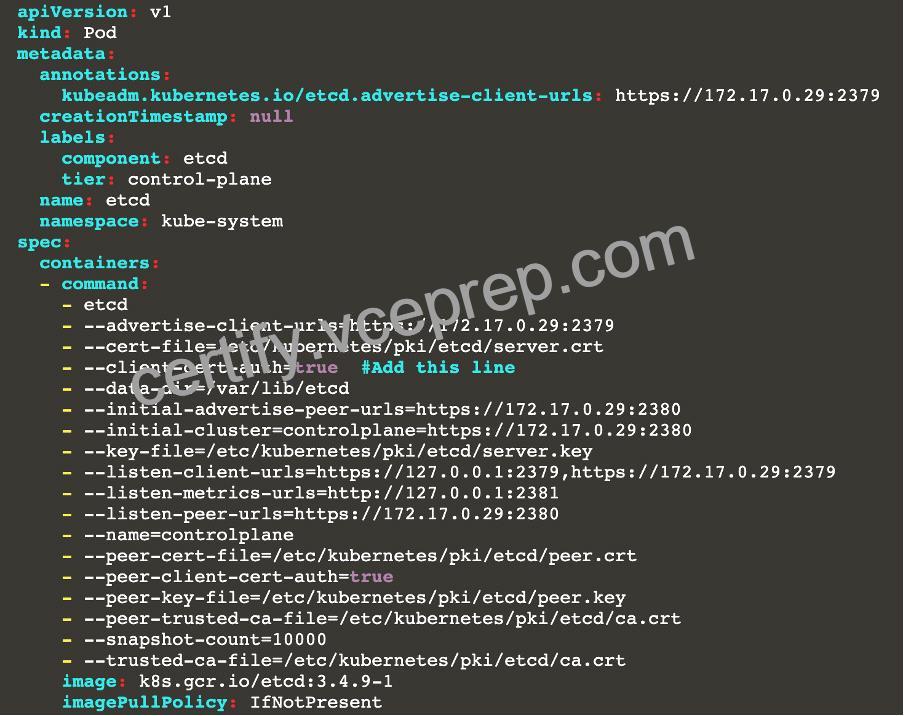
2.2 Ensure that the client-cert-auth argument is set to true
worker1 $ vim /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml
anonymous:
enabled: true #Delete this
enabled: false #Replace by this
authorization:
mode: AlwaysAllow #Delete this
mode: Webhook #Replace by this
worker1 $ systemctl restart kubelet. # To reload kubelet config
ssh to master1
master1 $ vim /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml
– — authorization-mode=Node,RBAC
master1 $ vim /etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd.yaml
– –client-cert-auth=true
Explanation
ssh to worker1
worker1 $ vim /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: true #Delete this
enabled: false #Replace by this
webhook:
cacheTTL: 0s
enabled: true
x509:
clientCAFile: /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
authorization:
mode: AlwaysAllow #Delete this
mode: Webhook #Replace by this
webhook:
cacheAuthorizedTTL: 0s
cacheUnauthorizedTTL: 0s
cgroupDriver: systemd
clusterDNS:
– 10.96.0.10
clusterDomain: cluster.local
cpuManagerReconcilePeriod: 0s
evictionPressureTransitionPeriod: 0s
fileCheckFrequency: 0s
healthzBindAddress: 127.0.0.1
healthzPort: 10248
httpCheckFrequency: 0s
imageMinimumGCAge: 0s
kind: KubeletConfiguration
logging: {}
nodeStatusReportFrequency: 0s
nodeStatusUpdateFrequency: 0s
resolvConf: /run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf
rotateCertificates: true
runtimeRequestTimeout: 0s
staticPodPath: /etc/kubernetes/manifests
streamingConnectionIdleTimeout: 0s
syncFrequency: 0s
volumeStatsAggPeriod: 0s
worker1 $ systemctl restart kubelet. # To reload kubelet config
ssh to master1
master1 $ vim /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml
master1 $ vim /etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd.yaml